 |
am2zzw00012620
DTC P049B:00 [PCM (SKYACTIV-D)]
id0102t5856400
Details On DTCs
|
Description |
LP-EGR flow insufficient detected |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Detection condition
|
Determination conditions
|
• When the following condition is met, the LP-EGR volume is lower than the specification for 0.30 g/rev for a continuous 8.2 s.
|
|
Preconditions
|
• During LP-EGR control
• During HP-EGR control
• Fuel injection amount:15—50 mm3/stoke
• Engine speed: 1,300—6,000 rpm
• Engine torque: 70—240 N·m{7.2—24 kgf·m, 52—177 ft·lb}
• Target HP-EGR flow volume: 0.31―0.6 g/rev
• The following DTCs are not detected:
|
|
|
Drive cycle
|
• 2
|
|
|
Self test type
|
• CMDTC self test
|
|
|
Sensor used
|
• LP-EGR control valve
• HP-EGR control valve
• Intake shutter valve
• Exhaust shutter valve
• MAF sensor
• MAP sensor
• Boost air temperature sensor
• Exhaust gas pressure sensor No.1
• Exhaust gas temperature sensor No.1 etc.
|
|
|
Fail-safe
|
• Not applicable
|
|
|
Vehicle status when dtcs are output
|
• Check engine light is illuminated
|
|
|
Possible cause
|
• Erratic signal to PCM
• HP-EGR system malfunction
• Exhaust shutter valve malfunction
• LP-EGR control valve malfunction (stuck close)
• Exhaust shutter valve position sensor (built-into exhaust shutter valve) malfunction
• LP-EGR control valve position sensor (built-into LP-EGR control valve) malfunction
• EGR cooler clogged
• Catalytic converter or diesel particulate filter malfunction (deformation, damage)
• Exhaust gas leakage from LP-EGR system
• LP-EGR system passage malfunction (restriction)
• Air suction in intake air system between turbocharger and intake manifold
• PCM malfunction
|
|
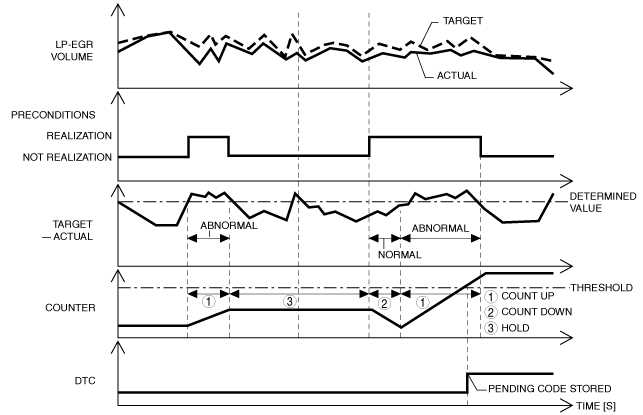
System Wiring Diagram
Function Explanation (DTC Detection Outline)
am2zzw00012620
|
Repeatability Verification Procedure
PID Item/Simulation Item Used In Diagnosis
PID/DATA monitor item table
|
Item (definition) |
Reference |
|---|---|
|
CHARGE_AIR_COOL_TEMP
|
|
|
EX_PRES
|
|
|
EX_GAS_TEMP_1
|
|
|
MAP
|
|
|
MAF
|
Function Inspection Using M-MDS
|
Step |
Inspection |
Results |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY RELATED REPAIR INFORMATION OR SERVICE INFORMATION AVAILABILITY
• Verify related Service Bulletins, on-line repair information, or Service Information availability.
• Is any related Information available?
|
Yes
|
Perform repair or diagnosis according to the available information.
• If the vehicle is not repaired, go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
2
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY DTC CAUSING FREEZE FRAME DATA
• Is DTC P049B:00 causing the freeze frame data?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Inspect the DTC causing the freeze frame data.
(See DTC TABLE [PCM (SKYACTIV-D)].)
|
||
|
3
|
PURPOSE: RECORD VEHICLE STATUS WHEN DTC WAS DETECTED TO UTILIZE WITH REPEATABILITY VERIFICATION
• Record the freeze frame data/snapshot data.
|
—
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
4
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY OTHER RELATED DTCs
• Perform the DTC inspection for the PCM.
(See DTC INSPECTION)
• Are any other DTCs displayed?
|
Yes
|
Repair the malfunctioning location according to the applicable DTC troubleshooting.
(See DTC TABLE [PCM (SKYACTIV-D)].)
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
5
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF THERE IS PID ITEM CAUSING DRASTIC CHANGES OF ACCELERATION FLUCTUATION BY INPUT SIGNAL TO PCM
• Access the following PIDs using the M-MDS:
(See DTC INSPECTION.)
PCM:
• Is there any signal that is far out of specification?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure to perform the procedure from step 1.
|
||
|
6
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY CONNECTOR CONNECTIONS
• Access the following PIDs using the M-MDS:
(See DTC INSPECTION.)
PCM:
• When the following parts are shaken, does the PID value include a PID item which has changed?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the applicable connector parts.
Go to the troubleshooting procedure to perform the procedure from repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure to perform the procedure from step 1.
|
Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure
|
Step |
Inspection |
Results |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
PURPOSE: IINSPECT EXHAUST SHUTTER VALVE POSITION SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Inspect the exhaust shutter valve, then go to repair completion verification.
|
||
|
2
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT LP-EGR CONTROL VALVE CONTROL SYSTEM OPERATION
• Perform the LP-EGR Control Valve Operation Inspection.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
3
|
PURPOSE: IINSPECT LP-EGR CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
4
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT INTAKE AIR SYSTEM FOR AIR SUCTION
• Inspect for air leakage at the following:
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
5
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT FOR RESTRICTION OR CLOGGED IN HP-EGR PASSAGE
• Switch the ignition off.
• Remove the HP-EGR control valve.
• Visually inspect the HP-EGR passage for clogging and the gasket correctly installed.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to the next step.
(If there is clogging caused by soot in the HP-EGR control valve, inspect around the HP-EGR piping and clean or replace it.)
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
6
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT EGR COOLER
• Inspect the EGR cooler for clogging.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
7
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT LP-EGR SYSTEM FOR LEAKAGE
• Visually inspect for exhaust gas leakage from the LP-EGR system.
• Is there any leakage?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
8
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT FOR RESTRICTION IN LP-EGR SYSTEM PASSAGE
• Switch the ignition off.
• Remove the LP-EGR control valve.
• Visually inspect the LP-EGR passage for restriction and the gasket correctly installed.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to the next step.
(If there is restriction caused by soot in the LP-EGR control valve, inspect around the LP-EGR piping and clean or replace it.)
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
Repair completion verification 1
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY THAT VEHICLE IS REPAIRED
• Install/connect the part removed/disconnected during the troubleshooting procedure.
• Clear the DTC recorded in the memory.
(See CLEARING DTC.)
• Replicate the vehicle conditions at the time the DTC was detected using the following procedure.
• Perform the DTC inspection for the PCM.
(See DTC INSPECTION.)
• Is the same Pending DTC present?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
If the CAN communication is normal, perform the diagnosis from Step 1.
• If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM, then go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
Repair completion verification 2
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF OTHER DTCs DISPLAYED
• Perform the DTC inspection.
(See DTC INSPECTION.)
• Are any other DTCs displayed?
|
Yes
|
Repair the malfunctioning location according to the applicable DTC troubleshooting.
|
|
No
|
DTC troubleshooting completed.
|